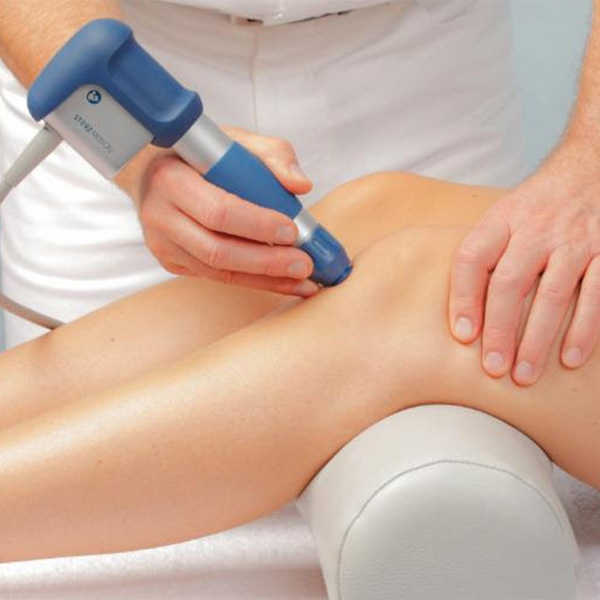
Shockwave Therapy
If you’ve ever struggled with an injury or dealt with an ache that just wouldn’t mend, your body might have benefited from extra help during the healing process.
Learn More




If you’ve ever struggled with an injury or dealt with an ache that just wouldn’t mend, your body might have benefited from extra help during the healing process.
Learn More
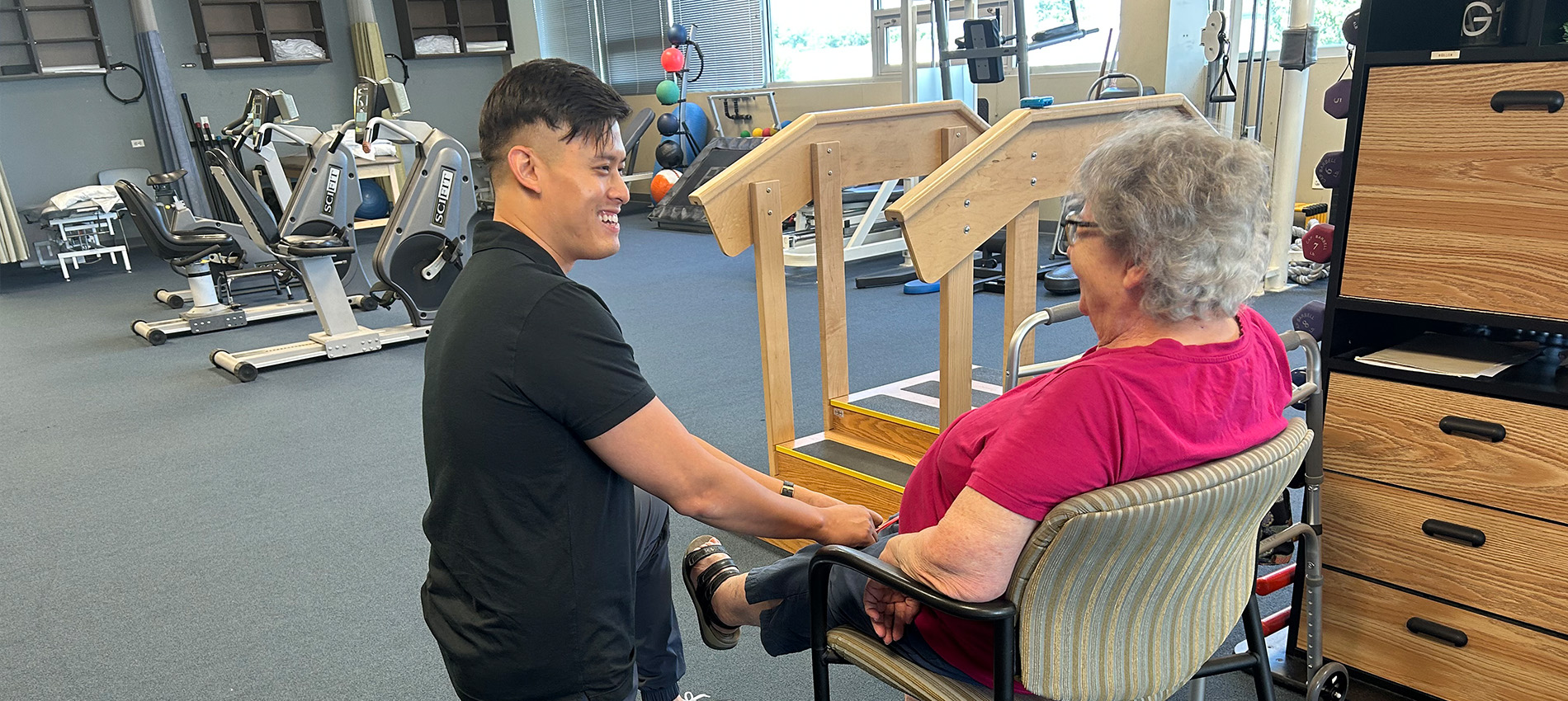
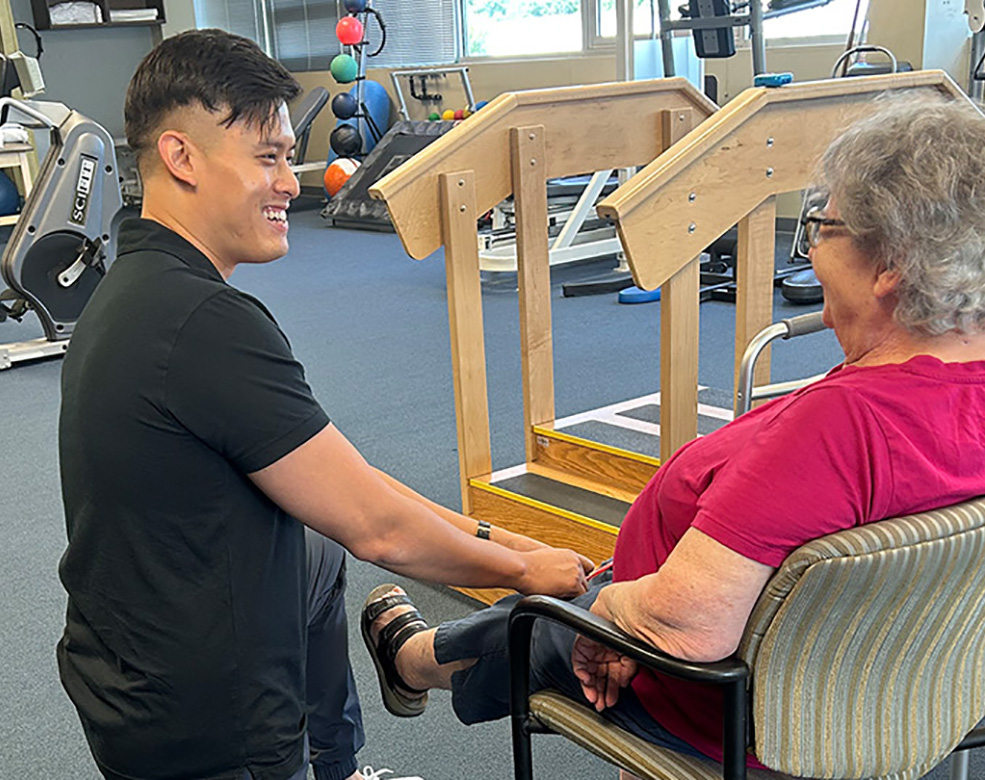
Physical therapists are movement experts who treat people of all ages and abilities, helping them to improve and maintain function and quality of life.
Learn More

At Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation our main focus is to help people recover from injuries to the hands and the “upper quarter” of the body. These injuries can occur in accidents, when people have surgery, as symptoms of chronic illnesses and pain or as a repetitive stress injury.
Learn More

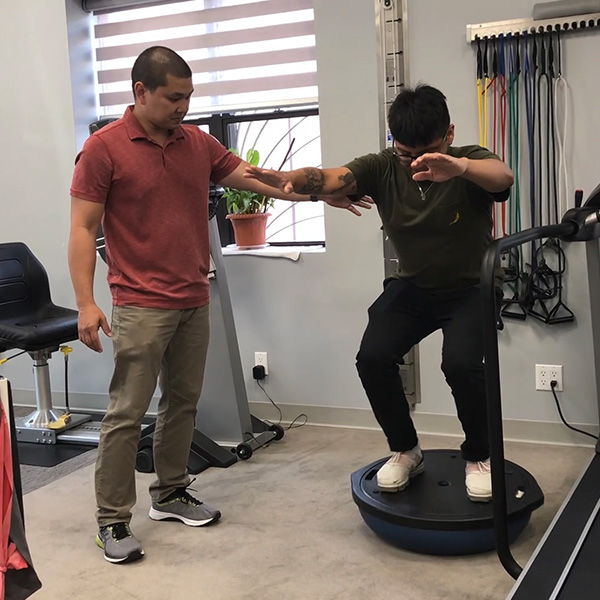
At The PMR Center we understand that staying in shape should be an important component in everyone's life. Unfortunately, not everyone can adapt to traditional exercise facilities. This is where our Supervised Fitness Programs can help.
Learn More

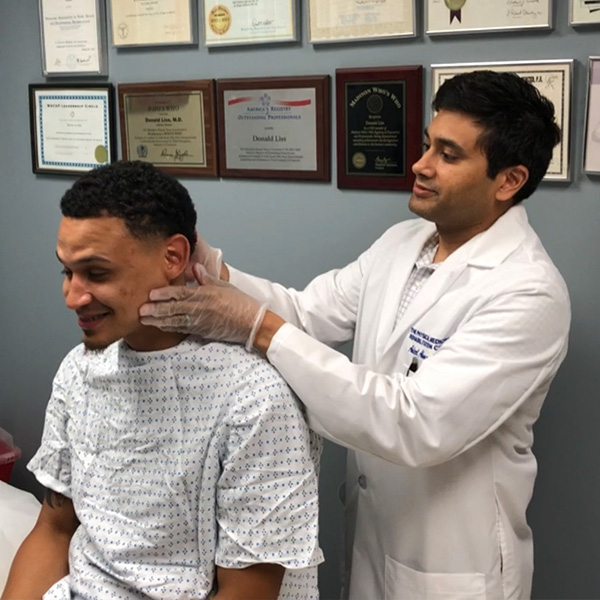
Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation (Physiatry) is a specialty of medicine concerned with the diagnosis and treatment of aches and pains and other disabling conditions.
Learn More

Our commitment to enhance patient-doctor communication led us to create a center where doctors and therapists work together for a carefully coordinated level of patient care that’s truly unique.
Learn More

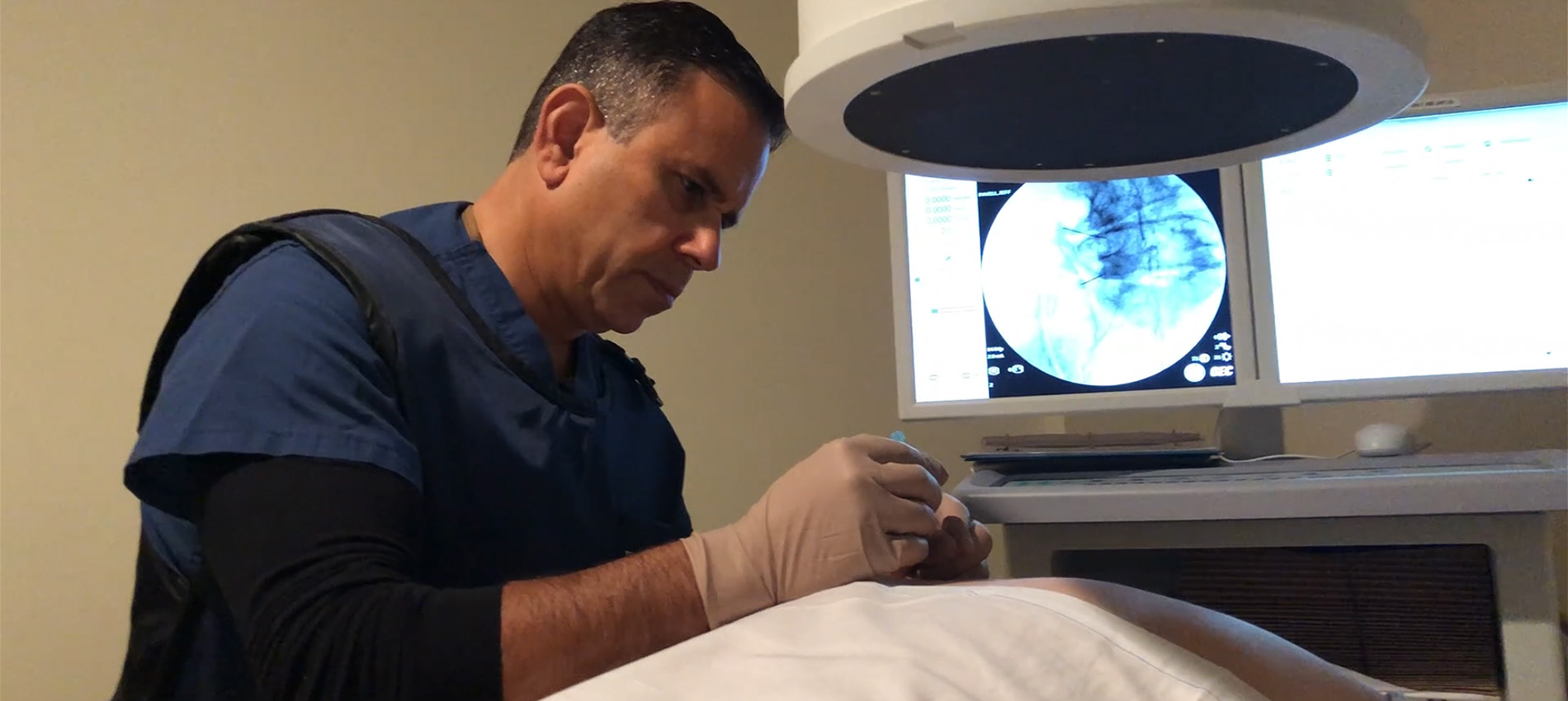
Epidural Steroid Injection has been found to be an effective adjunct to treatment for patients with neck, lower back, arm, and leg pain. Their primary use is as one component of a comprehensive treatment plan that includes medication, physical therapy, and education in body mechanics.
Learn More
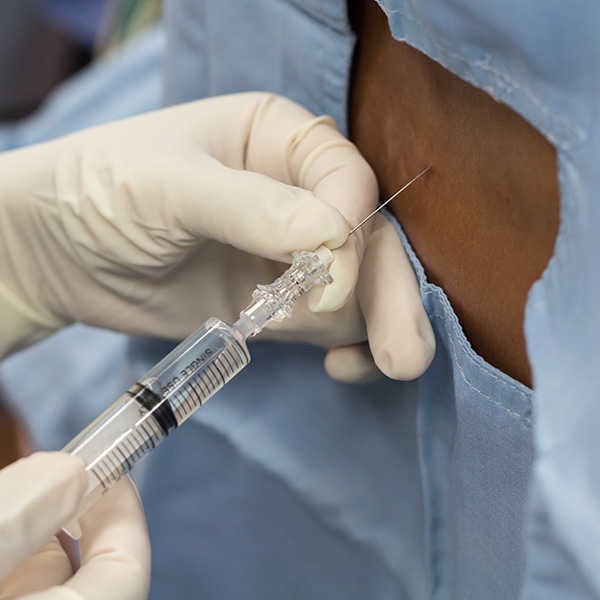
Some causes of knee pain, including pain due to osteoarthritis, can be treated with injections of gel into the knee. This is known as viscosupplementation. It is often used in concert with physical therapy, and possibly after steroid injections have been utilized.
Learn More
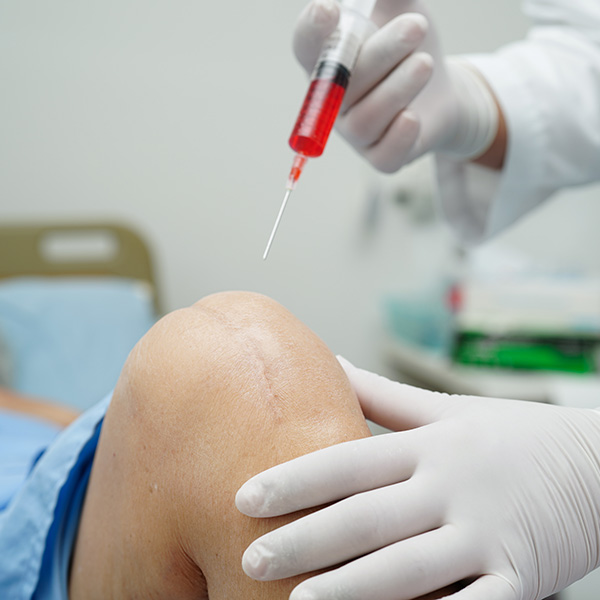
Prolotherapy, also known as Regenerative Injection Therapy, is an injection technique used to treat chronic pain related to damage to underlying ligament and/or tendon structures. Prolotherapy is used successfully to treat many different paintful conditions.
Learn More
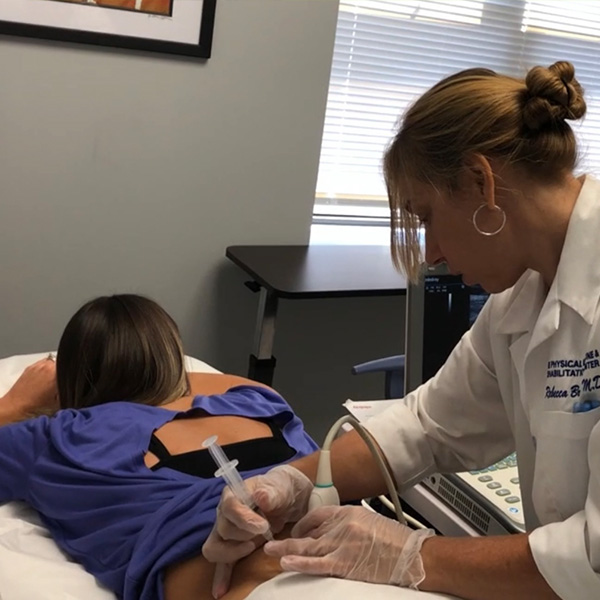
EMG stands for electromyography, which is a test of the function of the muscles in the body. An EMG test is almost always performed along with a test of the nerves, known as nerve conduction studies (NCS). Together, EMG and NCS are called electrodiagnostics.
Learn More

OMT is a form of non invasive hands on manual medicine which focuses on treating the body’s interconnected system of bones, muscles, and nerves. Osteopathic physicians (DO’s) have undergone special training in the musculoskeletal system.
Learn More

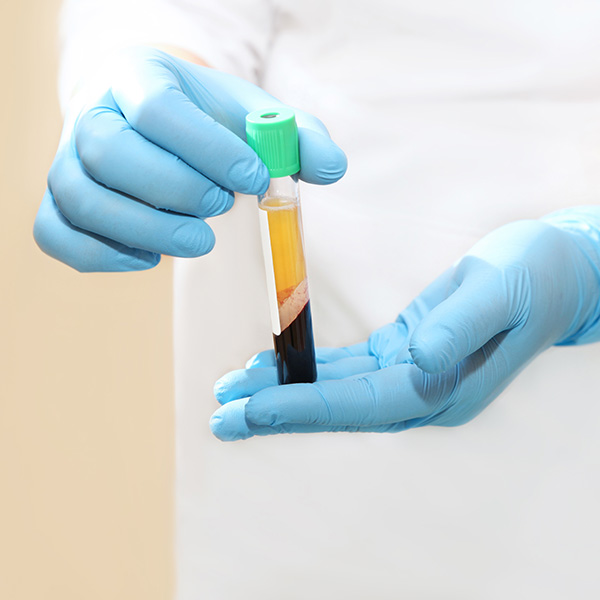
Platelet rich plasma (PRP) is derived from your own blood. Your blood is mainly liquid and contains small solid components including red and white blood cells along with platelets. Platelets are integral in blood clotting.
Learn More
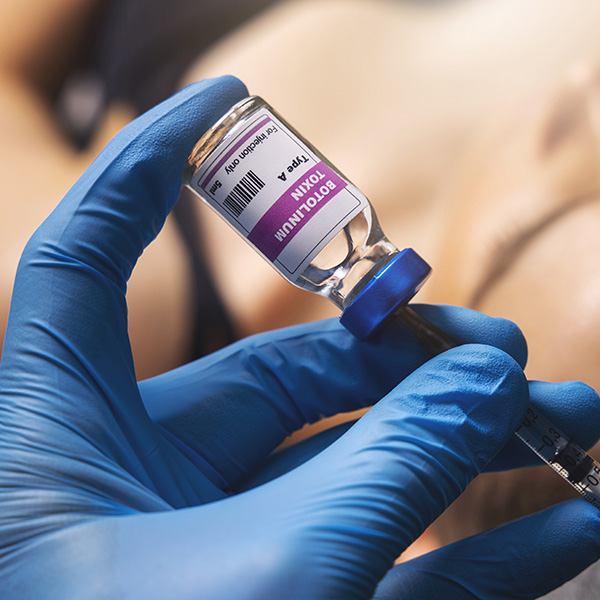
Spasticity is a condition characterized by increased muscle tone and stiffness, often resulting from neurological disorders like cerebral palsy, multiple sclerosis, or stroke. It can cause muscle tightness, pain, and difficulty with movement. Botulinum toxin injections have been found to be effective in reducing spasticity and improving functional abilities in affected individuals.
Learn More
Acupuncture is an ancient healing technique that involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to promote natural healing and alleviate various health issues, including pain and stress.
Learn More

Vestibular therapy, also known as vestibular rehabilitation therapy (VRT), is a specialized form of physical therapy focused on treating disorders of the vestibular system, which controls balance and spatial orientation. hrough tailored exercises and techniques, VRT aims to alleviate symptoms like dizziness and vertigo caused by vestibular dysfunctions.
Learn More

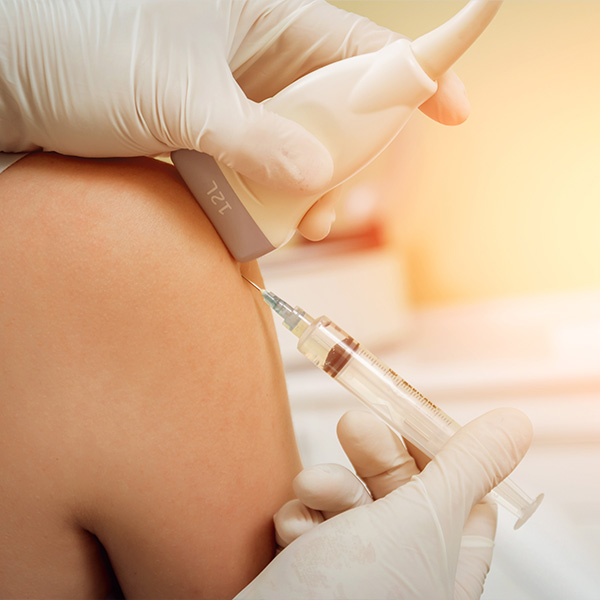
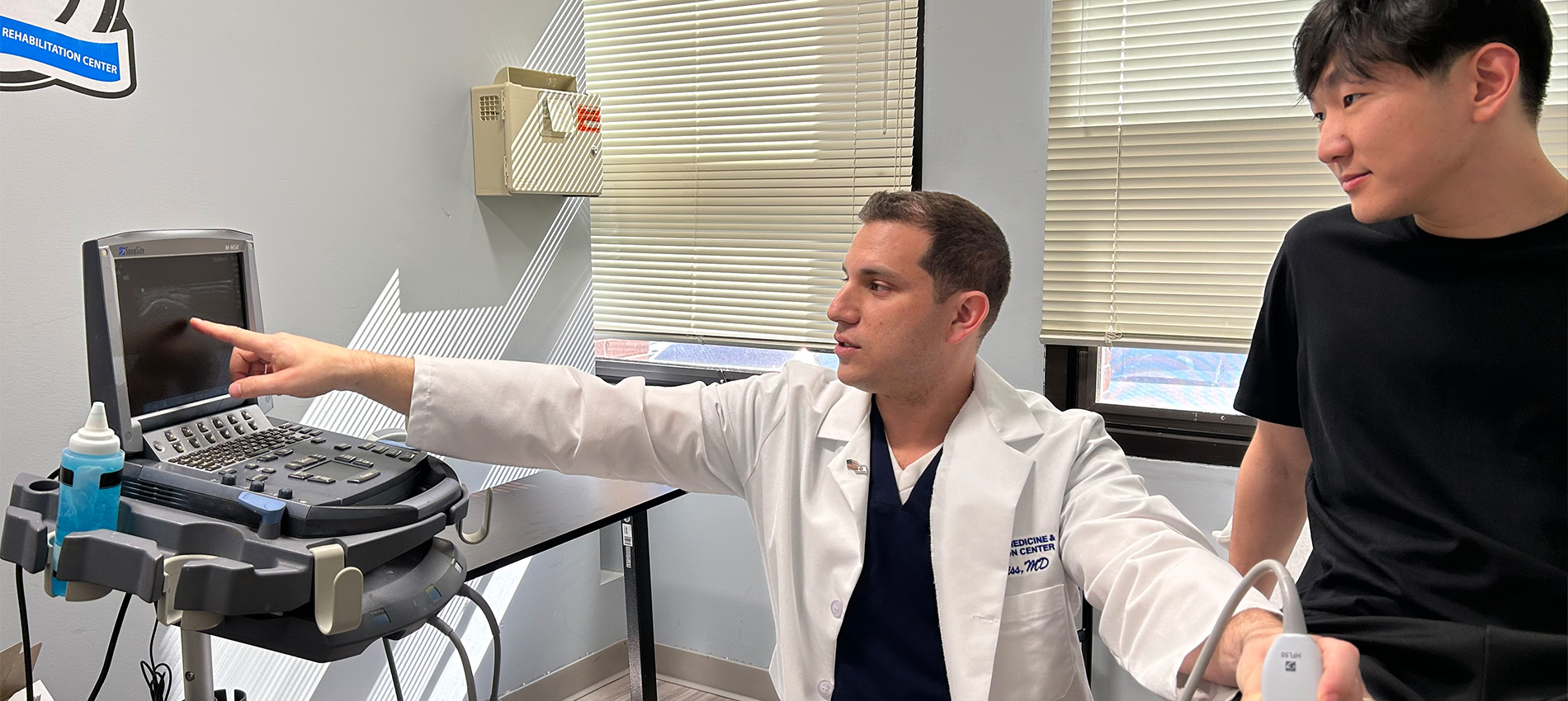
Our providers use real-time ultrasound imaging to precisely guide the placement of a needle for injections or aspirations. This technique enhances the accuracy and safety of the procedures.
Learn More